Examples Gallery
Explore interactive WebGPU shaders built with ralph-gpu. Click any example to open it in the playground and experiment with the code.

Simple Gradient
The simplest possible shader — map UV coordinates to colors. This creates a gradient from black (bottom-left) to cyan (top-right).
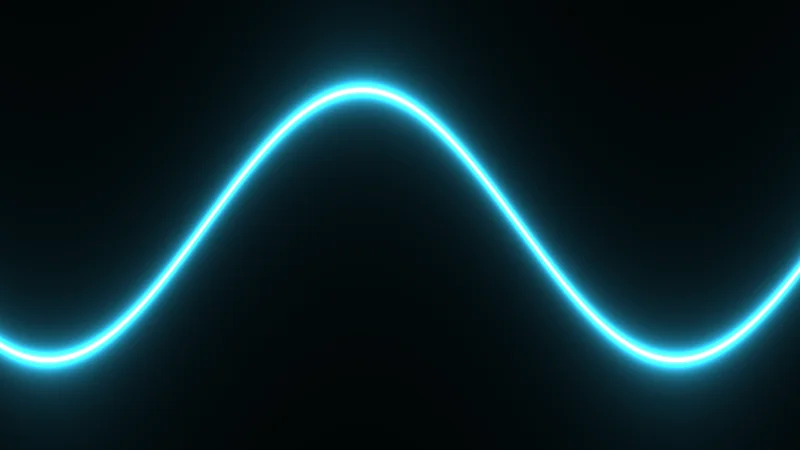
Animated Wave
A glowing sine wave with custom uniforms. The wave animates over time using globals.time.
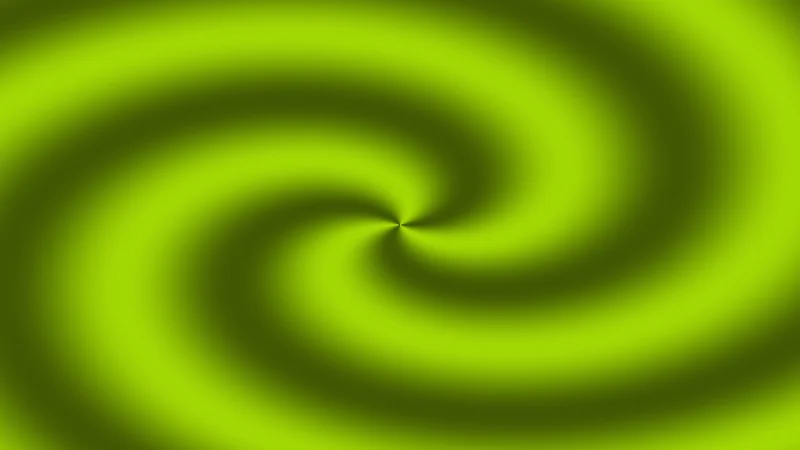

Time-Based Color Cycling
A hypnotic pattern that cycles through colors over time. Combines time, distance, and angle for a mesmerizing effect.

Raymarching Sphere
A basic 3D sphere rendered using raymarching. This demonstrates how to create 3D shapes and lighting entirely within a fragment shader.
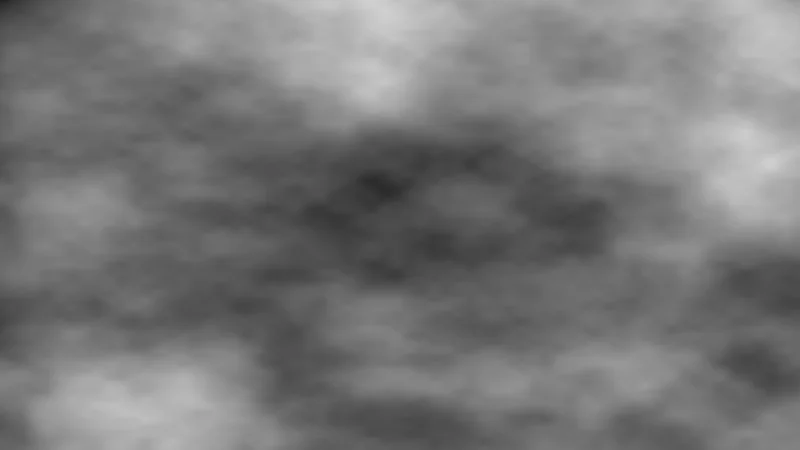

Perlin-style Noise
Layered fractional Brownian motion (fBm) noise. This technique is fundamental for generating procedural textures, terrain, and natural-looking patterns.

Metaballs
Organic-looking "blobs" that merge together based on an implicit surface. This effect uses a distance-based field and a threshold to create smooth blending.
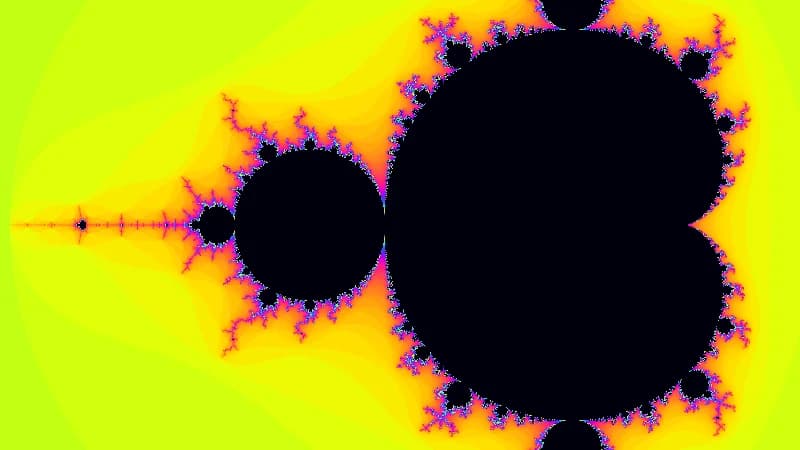

Mandelbrot Set
The classic complex number fractal. This shader computes the set by iterating z = z² + c and mapping the escape time to vibrant colors.
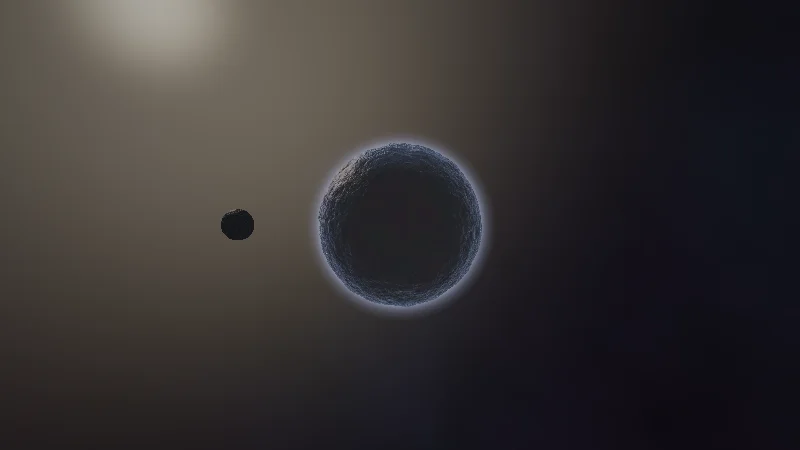

Alien Planet
A procedurally generated alien world with atmospheric scattering and an orbiting moon. Uses raymarching with fBm noise for terrain detail.
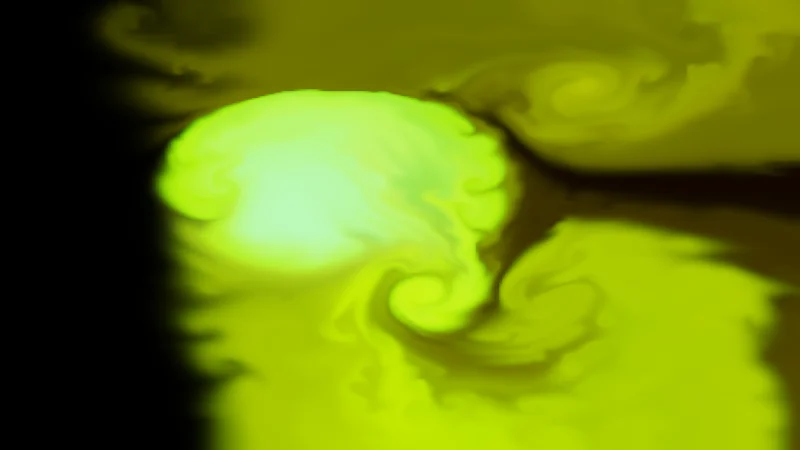

Fluid Simulation
Real-time Navier-Stokes fluid simulation using ping-pong buffers, vorticity confinement, and pressure projection.
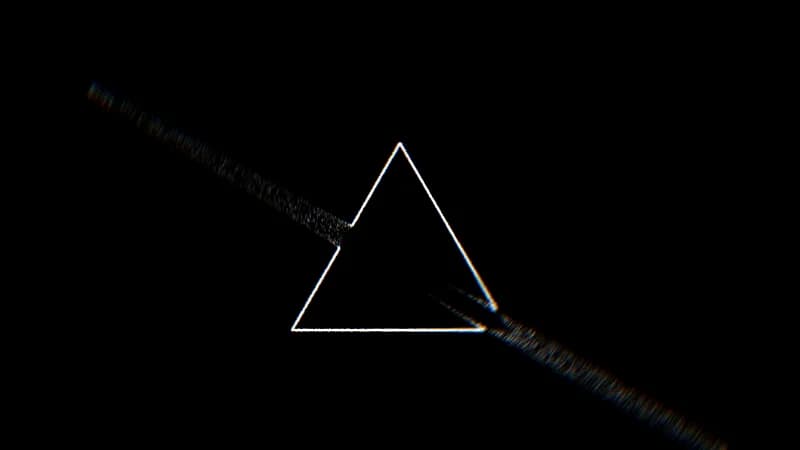

Triangle Particles
GPU-driven particle system with SDF-based physics. 30,000 particles spawn on triangle edges and flow along a signed distance field with chromatic aberration postprocessing.
Tips for Shader Development
🎨 UV Coordinates
Always normalize pixel coordinates: let uv = pos.xy / globals.resolution. This gives you values from 0-1 which are easier to work with.
⏱️ Time Animation
Use globals.time for smooth animation. For physics, use globals.deltaTime to stay frame-rate independent.
🔧 Debugging
Output intermediate values as colors to debug: return vec4f(myValue, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0). Red channel shows your value visually.
📐 Aspect Ratio
For circular effects, correct for aspect ratio: let centered = (uv - 0.5) * vec2f(globals.aspect, 1.0)